By Ivan Rodriguez
The Oil & Gas industry is one of the sectors that consumes the most water in its industrial processes. With the increase in unconventional reservoirs and regulations aimed at promoting more responsible water use and disposal, operators are currently facing a dual challenge: meeting stringent environmental limits while maintaining economic efficiency in a highly volatile price environment.
Several states, including Texas, Colorado, and North Dakota, are implementing increasingly strict regulations, and simply disposing of water in injection wells is no longer sufficient. The trend is moving toward responsible reuse.

Water Consortium.
In response to this shift, the industry has advanced toward more robust treatment schemes. The combination of mechanical and chemical processes can achieve removal levels of up to 95% for dispersed hydrocarbons and fine solids. At the same time, technologies such as membranes and nanofiltration are increasingly being applied in projects aimed at reusing produced water, thereby reducing the reliance on fresh water sources. This approach addresses not only operational needs
but also growing social and regulatory pressure regarding the sustainable management of water resources.
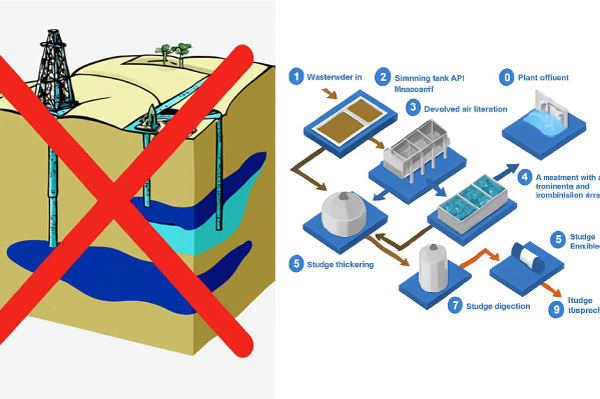
industry.
Source: Image edited and composed by the author (ChatGPT), 2025.
All these alternatives and emerging technologies are driving the use of simulation tools during the engineering process to support decision-making in equipment selection. While data interpretation and initial equipment selection remain the engineer’s responsibility, these tools streamline the recreation of different operational scenarios that may occur during the evaluation of a given solution.
The ability to simulate changing conditions allows engineers to assess equipment performance under varying operating parameters and to anticipate real operational behavior in a safe and controlled environment. This makes it possible to test different equipment combinations to determine the optimal solution in terms of both the number of units and removal efficiency.
Simulation tools are also highly valuable not only for the development of new projects but also when modifying existing equipment. The ability to test different scenarios and make internal modifications—whether by adding or removing components—before carrying out physical interventions is critical. This capability allows engineers to evaluate the outcome of modifications without putting the equipment at risk and while minimizing the economic impact associated with
trial-and-error approaches..
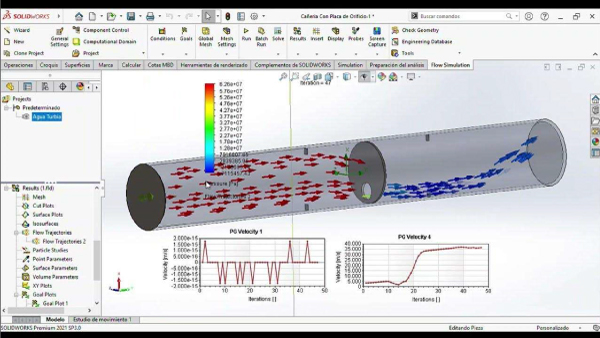
video “Oil and Gas Water Treatment Plant”, 2025
Ultimately, adopting advanced treatment technologies and complementing their implementation with engineering simulation tools provides a significant advantage: it enables operators to evaluate multiple operational scenarios before committing to real investments, optimize equipment selection and configuration, and anticipate system behavior under changing conditions.
This approach not only improves the technical and economic efficiency of projects but also strengthens companies’ ability to adapt to stricter regulations and respond to growing social expectations regarding responsible water resource management.


